

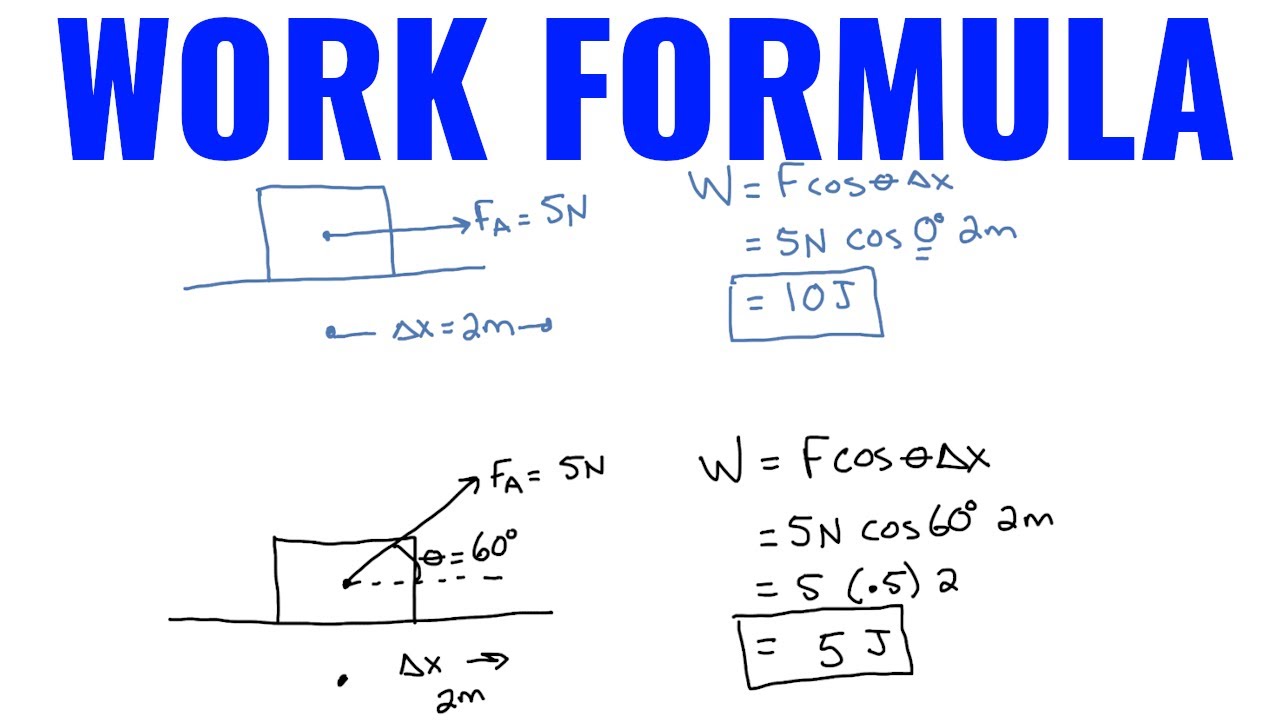
For the first part of her trip, she exerts 300 N of force to move a suitcase 16 meters vertically so the amount of work done is: There are two main portions of her trip, so we can calculate the work done over each portion individually, then, combine the two values to get the total amount of work done. How much work was done over her whole trip? She then pushes the suitcase with 100 N of force the remaining 8 meters to her hotel room. Linda takes a 300 N suitcase up 3 flights of stairs for a total vertical distance of 16 meters. So the 64 N force at a 120° angle did 156.32 joules of work moving the book 3 meters. So plugging these values into our handy equation yields: We also know that there is a 120°angle between the angle of the direction of applied force and the direction of motion. In this case, we know the force of 64 N and the distance of 3 m. A 64 N force is applied to the book at a 120° angle from horizontal and moves the book 3 meters in the horizontal direction. So, the 100 N force did 500 joules work moving the block 5 meters. So we plug these values into our equation We also know that since the force is applied in the same direction as the displacement, Θ is equal to 0. In this case, we know the force is 100 N and the distance is 5 meters. Example problems (1)Ī 100 Newton force is applied to a 15kg box in the horizontal direction and moves it 5 meters horizontally.
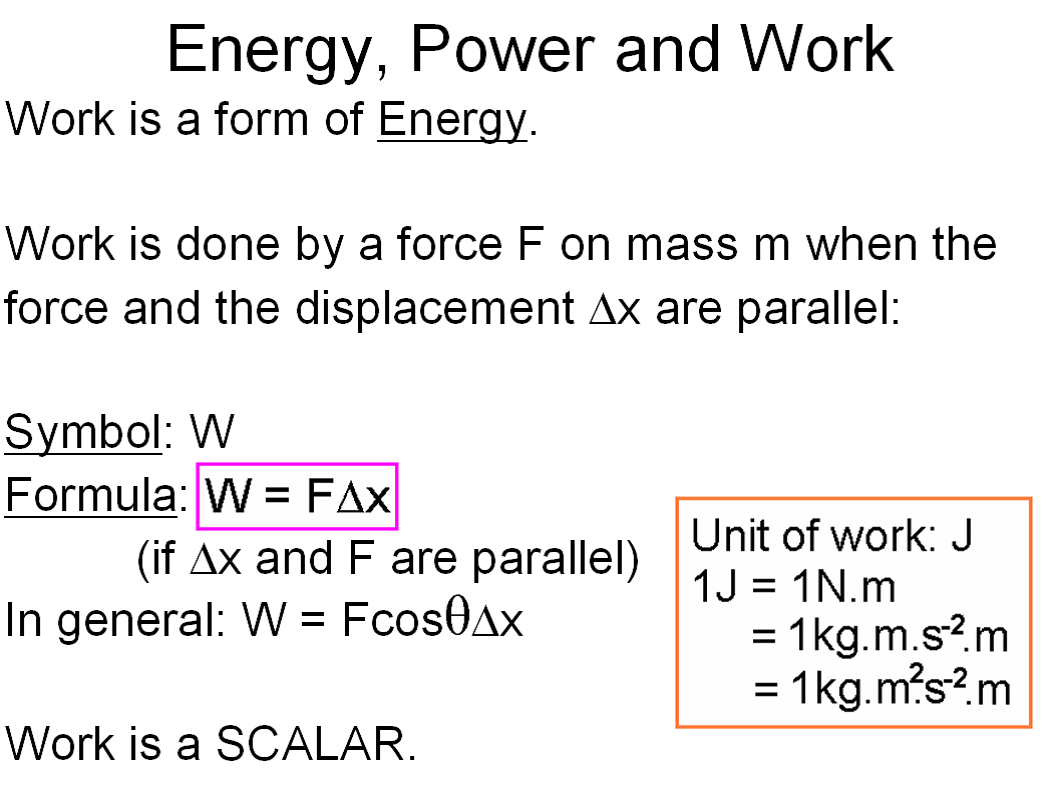
Let’s consider some simple examples to illustrate the concept of work. So the force from a person pushing the side of a skyscraper is not doing any work as the skyscraper does not move. In cases where a force is applied to an object but does not move it, no work has been done. When a ball rolls down a hill due to the force of gravity, when you pick up your backpack off the ground, when your car’s internal engine applies a force to make your wheels move all of these events involve a force moving an object over a distance and so involve some work. Whenever a force moves an object, we say that work has been done. Another way to understand it is that one joule is equivalent to the amount of energy transferred when one newton of force moves an object a distance of one meter. The SI unit for work is the joule ( J), and its dimensions are kg Where W is the amount of work, F is the vector of force, D is the magnitude of displacement, and Θ is the angle between the vector of force and the vector of displacement. The general formula for work and for determining the amount of work that is done on an object is: The amount of work a force does is directly proportional to how far that force moves an object. In other words, work is equivalent to the application of a force over a distance.
In physics we can define energy as the capacity to do work.In physics, we say that a force does work if the application of the force displaces an object in the direction of the force. This energy is now called the kinetic energy of a moving body and its formula was derived directly from Newtons work equation. The next simplest case is when the force is a linear function of x. The force and the displacement are given in the problem statement. The electric field performs work on the particle. There are several special cases that are worth noting.įirst when the force is constant and is parallel to the displacement x the above equation simplifies to.įor the sake of simplicity we will consider the. In physics we say that a force does work if the application of the force displaces an object in the direction of the forceIn other words work is equivalent to the application of a force over a distance. LatextextWDelta textKEfrac12 textmv_textf2-frac12 textmv_texti2latex where v i and v f are the speeds of the particle before and after the application of force and m is the particles mass. The change in voltage is defined as the work done per unit charge against the electric fieldIn the case of constant electric field when the movement is directly against the field this can be written. The magnitude of the force form the formula of work done it is evident that the higher the magnitude of force the work done will be higher and vice-versa. This equation is one form of the work-energy equation and gives us a direct relation between the net work done on a particle and that particles velocity. In our everyday language work is related to expenditure of muscular effort but this is not the case in the language of physics.Įlectric field work is the work performed by an electric field on a charged particle in its vicinity.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
